US Air Quality Gradebook
Emission
Gradesheets
![]()
|
The emission gradesheets, which are accessible through hyperlinks below, consider county-by-county air emission densities, in tons per square mile per year, of the following pollutants: carbon monoxide (CO), lead and lead compounds (Pb), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOC), particulate matter less than or equal to 10 micrometers (PM10), particulate matter less than or equal to 2.5 micrometers (PM2.5), ammonia (NH3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), total hazardous air pollutants (HAP), and two particular HAP’s, namely diesel emissions and acrolein emissions. For the first eight pollutants except lead and its compounds, (CO through SO2, except Pb), emissions are based on 1999 data from the EPA National Emissions Inventory at https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories, and in particular at https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/pollutant-emissions-summary-files-earlier-neis. More recent data can be found at https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/national-emissions-inventory-nei. Lead, acrolein, diesel emissions, and hazardous air pollutants are 1996 data: see https://archive.epa.gov/airtoxics/nata/ |
For more recent data see https://www.epa.gov/national-air-toxics-assessment, and in particular https://www.epa.gov/national-air-toxics-assessment/2014-nata-assessment-results. For a discussion of hazardous air pollutants see https://www.epa.gov/haps, and for a list of them see https://www.epa.gov/haps/initial-list-hazardous-air-pollutants-modifications. Diesel emissions top the list of air pollutants adding to cancer risk. Acrolein (CH2CHCHO, pronounced a-kro’-lee-in, “acrid+olein”) is the dominant air pollutant for noncancer hazard. It is an air pollutant produced by forest and wildfires, open burns, structure fires, and as a combustion product of gasoline, diesel, and jet engines. One can find related consideration of these pollutants at online reference http://www.scorecard.org/, and specifically at http://www.scorecard.org/ranking/. Scorecard ranks counties by total tons per county, rather than considering tons per square mile of a county’s total jurisdictional land and water area as here. For each US county, assign grade levels to emission densities, in tons per square mile per year, according to the following table: |
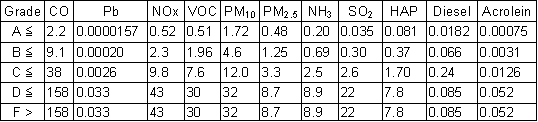
|
The grade "A" represents the Best/Cleanest emission densities in the US, and "F" the Worst/Dirtiest in the US. The grades reflect the statistical distribution |
of base-10 logarithms of the measured emission densities for all US counties, as in the following tables: |


|
The shift of the bell curve by one standard deviation for
lead reflects a cleaner national average for this pollutant. The
statistical procedure makes each grade limit a common multiple of the next
lower limit. For example, the upper grade A limit for VOC before
"rounding up" is 0.505 tons per square mile per year, and the
common multipler for the VOC distribution is 3.87 |
The unrounded upper limit for When applied individually to the 11 emissions, the procedure results in the following percentages of measured counties in the grade levels: |
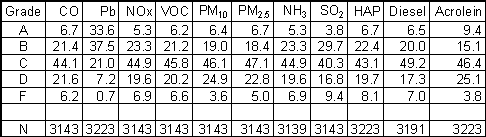
|
[N = Number of US counties with emissions data for the pollutant. Example: Grade D for CO means at least 72.2% of 3143 US counties have smaller CO emission densities (72.2% = 6.7% A's + 21.4% B's + 44.1% C's).] |
|
The hyperlinks below bring up sheets showing grades for each type of emission, the overall ambient grade, and the resultant county grades. There are two county grades, "self" for the county as determined by its own emission and ambient grades, and "map" for the county as affected by neighboring counties. (See "Maps" for more discussion on map grades.) One can use the grade sheets to determine which individual grades caused a county to be at the level it is. These are highlighted in bold |
italics. If the cause is a neighboring county, the "map" grade is highlighted. If the cause is ambient monitoring, one can further look in "Ambient Grade Sheets" to determine the specific pollutant measurement that determined the county's ambient grade. Click on a state, county-range combination to bring up that grade sheet. After viewing, click the browser's back button/arrow to return to this index page. |
Return to Air Quality Homepage